|
| Summary of Content |
| I used this set of really useful
tables to see how my first CSS turned out. What an education! I got more out
of tinkering with this page than I had out of numerous tutorials. See the
original at
Tampabay.rr.com. My thanks to B.Merkley. The content of these tables has been invaluable. |
| Basic Concepts | |
| Grouping |
Grouping allows the author to assign a single style declaration to multiple elements (selectors). Example: Sets Headings 1, 2, 3, & 5 to purple H1, H2, H3, H5 {color: purple;} |
| Class (tag attribute) |
Class selectors may be used as an attribute to a tag. A class selector is a string preceded by a period. Do not use the period when referencing the class. Do not begin a class name with a number, although IE4+ let you get away with it.
.example {color: red;}
<P class="example">This is an example in red.</P>
|
| ID (tag attribute) |
ID selectors may be used as an attribute to a tag. An ID selector is a string preceded by a hash mark (#), and is called using the ID= attribute. The hash mark does not appear in the value of ID. Works like the class selector except that the ID can be used only once in the document.
#i5 {color: red;}
<P ID="i5">This is text with an ID of 'i5'.</P>
|
| Contextual selectors |
Made up of one or more selectors delimited by spaces. The example rule indicates the bold mark-up will be red only while enclosed in H1 tags.
H1 B {color: red;}
<H1>This is <B>red</B>.</H1>
<P>This is <B>not</B>.</P>
|
| Comments |
Good idea to leave comments in the style sheet. Affects anything enclosed, even across multiple lines. /* This is a comment. */ |
| DIV and SPAN tags |
These two HTML tags were introduced to support style sheets.
Think of them as empty tags which you fill with styles. <DIV align=center><H1>This heading</H1></DIV> SPAN is used for inline formatting.
<SPAN class="example">red text in paragraph</SPAN>
|
| Units | |
| Length Units | Units of measure take 2-letter abbreviations, with no space
between number and unit.
width: 50px; margin-left: 2em; |
| Percentage Units |
Used by various properties to define size in relative terms. Values are calculated with regard to their context; in the example, the H2 element will be 75% of its default size.
H2 {font-size: 75% }
|
| Keywords |
CSS uses keywords as values for many properties. |
| Color Units |
By number; by percentage; by name. color: #FF00FF; /* note that this may be expressed as #F0F */ color: rgb(100%,0%,100%); color: chocolate |
| URLs |
Used by various properties to define the location of images. Important: Partial URLs are relative to the style sheet, not the HTML document! url(picture.gif) url(http://www.pix.org/lib1/pic278.gif) list-style-image: url(bullet3.gif) |
| The Cascade | |
| ! important | Style declaration is declared important. Important declarations
override all others, regardless of origin or specificity. In CSS2,
user will have precedence over author.H1 {color: maroon ! important;}
|
| Inheritance | Formatting properties of any element are inherited from the element in which it is contained. CSS properties always have some value, even if not specified by the author. This can be used to minimize style mark-up but can be the source of unpleasant surprises. |
| Link External Style Sheet | The external style sheet is the means to control the look of
many pages at once. Use the LINK tag in the HEAD of your page. Example: <LINK REL="STYLESHEET" TYPE="text/css" HREF="demo.css"> |
| Cascading Order and Style Syntax | Precedence is from the most specific to the most general. The
closer a style is to the element being styled, the more priority it
has. The order from highest to lowest:
|
| Media | Technically part of CSS-2, you can specify different styles for
online display and print. This works in IE4+ Windows and Opera
3.5. Important step toward single-sourcing!
<STYLE media="print"> /* print version styles here */
.noprint {display: none;} /* items with this class won't print */
</STYLE>
<STYLE media="screen"> /* screen version styles go here */
.noshow {display:none;} /* items with this class won't display */
</STYLE>
|
| Font Properties | |
| font-family | Used to declare specific font to be used, or a generic font
family in order of preference. The generic families are: serif, sans-serif, monospace, cursive and fantasy. They must not have quotes around them. Multiword font names should have quotes. P {font-family: "Times New Roman", serif;} |
| font-style | Selects between italic, oblique, and normal.
EM {font-style: italic;} |
| font-variant | Currently has two values: small-caps and normal. Likely to
acquire more values in the future.
H3 {font-variant: small-caps;} |
| font-weight | Values are: bold, normal, lighter, bolder and numeric values 100-900.
B {font-weight: 700;} |
| font-size | Sets the absolute size (pt, in, cm, px), relative size (em, ex),
or percentage of normal size. Keywords: xx-large, x-large, large, medium, small, x-small, xx-small, larger, smaller H2 {font-size: 200%;} H3 {font-size: 36pt;} |
| font | Shorthand property for the other font properties. The order of
values is important, and is as follows: font {font-style font-variant font-weight font-size/line-height font-family;}. Any of these values may be omitted but order is important. P {font: bold 12pt/14pt Helvetica,sans-serif;} |
| Color and Background Properties | |
| color | Sets the colour of a given element. For text, this sets the text
colour; for other elements, such as HR, it sets the foreground colour.
H6 {color: teal;} |
| background-color | Sets the background colour of an element. Background extends to
the edge of the element's border. Initial value: transparent.
{ background-color: #CCCC00 } |
| background-image | Sets an image to be the background pattern. In conjunction with
the other background properties, may tile or repeat in one
direction only. Recommend using with background-color to allow for
users who disable image loading.
BODY {background-image: url(bg41.gif);} |
| background-repeat | Sets the repeat style for a background image. Values are: repeat
(tile), no-repeat, repeat-x (horizontal), repeat-y (vertical). Default: repeat.
BODY { background-repeat: repeat-y } |
| background-attachment | Defines whether or not the background image scrolls with the element. Values are: scroll and fixed.
BODY {background-attachment: fixed;} |
| background-position | Sets the starting position of the background colour or image. If
a colour, the colour fill continues from the set position. If an
image, the first image is placed at the set position. Values:
Position (x y) or (x% y%); top, center, bottom, left, right.
BODY {background-position: top center;} |
| background | Shorthand property for the other background properties. The values can be written in any order.
BODY {background: white url(bg41.gif) fixed center;} |
| Text Properties | |
| word-spacing | Sets the amount of white space between words, which are defined
as strings of characters surrounded by white space.
P {word-spacing: 0.5em;} |
| letter-spacing | Sets the amount of white space between letters, which are
defined as any displayed character .
P {letter-spacing: 0.5em;} |
| text-decoration | Values are: none, underline, overline, line-through, blink. Combinations of the values are legal.
U {text-decoration: underline;}
.old {text-decoration: line-through;}
|
| vertical-align | Sets the vertical alignment of an element's baseline with
respect to its parent element's line-height. May only be applied to
inline elements; negative values are permitted. Keywords: baseline;
middle; sub; super; text-top; text-bottom.
.super {vertical-align: super;} |
| text-transform | Changes the case of the letters in the element, regardless of the original text. Values are: capitalize (capitalizes first letter of each word), uppercase, lowercase.
H1 {text-transform: uppercase;} |
| text-align | Sets the horizontal alignment of the text in an element. May only be applied to block-level elements.
P {text-align: justify;} H4 {text-align: center;} |
| text-indent | Sets the indentation of the first line in an element. Most often used to create a tab effect for paragraphs. Only applies to block-level elements; negative values are permitted.
P {text-indent: 5em;} H2 {text-indent: -25px;} |
| line-height | Sets the vertical distance between baselines in an element. Negative values are not permitted.
P {line-height: 18pt;} H2 {line-height: 200%;} |
| CSS Puts Everything in a Box | |
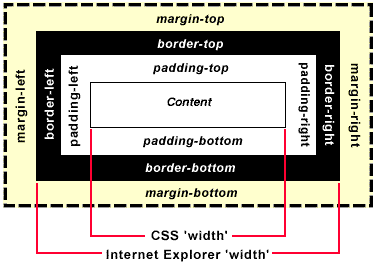
| The Box Model |
The most powerful way of thinking about style is to consider every element (<P>, <H1>,etc.) as a box. The dimensions of the box can be controlled to produce a very broad range of effects. If you think of a page as a box of boxes, this model forms the basis of positioning elements even to the pixel level. Note that as of IE6.0, that browser now follows the W3C definition for width, which should not include border and padding values.
|
| Box Properties | |
| margin-top | Sets the size of the top margin of an element. Negative values
are permitted, but exercise caution. Negative margins not handled
well by Netscape 4!
UL {margin-top: 0.5in;}
|
| margin-right |
Sets the size of the right margin of an element. Negative values are permitted, but exercise caution.
IMG {margin-right: 30px;}
|
| margin-bottom |
Sets the size of the bottom margin of an element. Negative values are permitted, but exercise caution.
UL {margin-bottom: 0.5in;}
|
| margin-left |
Sets the size of the left margin of an element. Negative values are permitted, but exercise caution.
P {margin-left: 3em;}
|
| margin |
Sets the size of the overall margin of an element. Negative values are permitted, but exercise caution. Multiple values start from the top and go clockwise.
H1 {margin: 2em;}
P {0% 5% 0% 5%;}
|
| padding-top |
Sets the size of the top padding of an element, which will inherit the element's background. Negative values are not permitted.
UL {padding-top: 0.5in;}
|
| padding-right |
Sets the size of the right padding of an element, which will inherit the element's background. Negative values are not permitted.
IMG {padding-right: 30px;}
|
| padding-bottom |
Sets the size of the bottom padding of an element, which will inherit the element's background. Negative values are not permitted.
UL {padding-bottom: 0.5in;}
|
| padding-left |
Sets the size of the left padding of an element, which will inherit the element's background. Negative values are not permitted.
P {padding-left: 3em;}
|
| Box Properties (cont.) | |
| padding |
Sets the size of the overall padding of an element, which will inherit the element's background. Negative values are not permitted.
H1 {padding: 2ex;}
|
| border-top-width |
Sets the width of the top border of an element, which will inherit the element's background, and may have a foreground of its own (see border-style). Negative values are not permitted.
UL {border-top-width: 0.5in;}
|
| border-right-width |
Sets the width of the right border of an element, which will inherit the element's background, and may have a foreground of its own (see border-style). Negative values are not permitted.
IMG {border-right-width: 30px;}
|
| border-bottom-width |
Sets the width of the bottom border of an element, which will inherit the element's background, and may have a foreground of its own (see border-style). Negative values are not permitted.
UL {border-bottom-width: 0.5in;}
|
| border-left-width |
Sets the width of the left border of an element, which will inherit the element's background, and may have a foreground of its own (see border-style). Negative values are not permitted.
P {border-left-width: 3em;}
|
| border-width |
Sets the width of the overall border of an element, which will inherit the element's background, and may have a foreground of its own (see border-style). Negative values are not permitted.
H1 {border-width: 2ex;}
|
| border-color |
Sets the color of the border of an element. In the example, top and bottom borders are silver, left and right are black. All 4 borders may be separately set.
H1 {border-color: silver black;}
|
| border-style |
Sets the style of the overall border of an element. Values: dashed; dotted; double; groove; inset; outset; ridge; solid; none. Default: none (border not displayed).
H1 {border-style: solid; border-color: purple;}
|
| Box Properties (cont.) | |
| border-top | Shorthand property which defines the width, colour, and style of
the top border of an element.
UL {border-top: 0.5in solid black;}
|
| border-right | Shorthand property which defines the width, colour, and style of
the right border of an element.
IMG {border-right: 30px dotted blue;}
|
| border-bottom |
Shorthand property which defines the width, colour, and style of the bottom border of an element.
UL {border-bottom: 0.5in grooved green;}
|
| border-left |
Shorthand property which defines the width, colour, and style of the left border of an element.
P {border-left: 3em solid gray;}
|
| border |
Shorthand property which defines the width, colour, and style of the overall border of an element.
H1 {border: 2px dashed tan;}
|
| width |
Used to set the width of an element. Can be used on any block-level or replaced element. Negative values are not permitted.
TABLE {width: 80%;}
|
| height |
Used to set the height of an element. Can be used on any block-level or replaced element, within limits. Negative values are not permitted.
IMG.icon {height: 50px;}
|
| float |
Causes the element to float to one side and other text to wrap around it. Use it for non-positioned block elements. Values: left; right; none.
IMG {float: left;}
|
| clear |
Specifies whether the element can have floating elements around it. Causes the element to be positioned below any floating elements on the side specified. Values: both; left; right; none. Default is none.
H1 {clear: both;}
|
| Classification Properties | |
| display |
Used to override default formatting for HTML elements. Values: block; inline; list-item; none. Default is block. Note that space is not reserved for the element when display = none. (See Positioning Property: visibility.)
.hide {display: none;}
|
| white-space |
Defines how whitespace within the element is treated. Values: normal, pre, nowrap.
TD {white-space: nowrap;}
TT {white-space: pre;}
|
| list-style-type |
Used to declare the type of bullet or numbering to be used in an unordered or ordered list. Values: disc; circle; square; decimal; lower-roman; upper-roman; lower-alpha; upper-alpha; none.
UL {list-style-type: square;}
OL {list-style-type: lower-roman;}
|
| list-style-image |
Used to declare an image to be used as the bullet in an unordered or ordered list. Applies to elements with a display value of list-item.
UL {list-style-image: url(bullet3.gif);}
|
| list-style-position |
Used to declare the position of the bullet or number in a list with respect to the content of the list item. Values: inside; outside. Default: outside.
LI {list-style-position: inside;}
|
| list-style |
Shorthand property condensing all other list-style properties. Applies to all elements with a display value of list-item.
UL {list-style: square url(bullet3.gif) outer;}
|
| Positioning Properties | |
| clip | Specifies an area of an element to be rendered transparent. Values: rect (top right left bottom) where top right left bottom are auto or length values (pt, in, cm, px)
{ clip: rect (5pt auto auto auto) }
|
| height |
Specifies the height of an element; the aspect ratio will be maintained if width is specified as auto. Values: auto or length values (pt, in, cm, px) or percentage.
{ height: 50px }
|
| width |
Specifies the width of an element; the aspect ratio will be maintained if height is specified as auto. Values: auto or length values (pt, in, cm, px) or percentage.
{ width: 50% }
|
| left |
Specifies the left position of an element positioned relatively or absolutely. Values: auto or length values (pt, in, cm, px) or percentage.
{ left: 2pt }
|
| top |
Specifies the top position of an element positioned relatively or absolutely. Values: auto or length values (pt, in, cm, px) or percentage.
{ top: -2pt }
|
| overflow |
Specifies how content which overflows its box is to be handled. Values: visible (display content); hidden (hide overflow content); scroll (provide scrolling mechanism); auto (up to the browser to figure out what to do)
{ overflow: auto }
|
| position |
Specifies whether the element can be positioned. Values: static (default--not positioned); relative (in relation to where the element would normally be); absolute (in relation to the top left hand corner of the parent element).
{ position: relative }
|
| Positioning Properties (cont.) | |
| visibility | Specifies whether element is visible. Note that space for element is reserved in either case. (see Classification Property: display) Values: visible; hidden.
{ visibility: hidden }
|
| z-index |
Specifies whether an element is displayed above or below overlapping elements. Values: auto (stack on page in order element appears in code); or an integer. Elements with higher numbers are on top of those with lower.
{ z-index: 2 }
|
| Pseudo-Classes and Pseudo-Elements | |
| anchor |
Pseudo-classes can be used in contextual selectors and can be combined with normal classes.
A:link {color: #900}
A:link IMG { border: solid blue }
A:hover{ background:#ffff00; } /*when mouse over link (IE4 only)*/
Below is a variation where you want the reader to know they are making a link outside your site. Define a class "external" to make the nature of the link obvious. Normal class names precede pseudo-classes in the selector.
A.external:link { color: magenta } |
| first-line | Applied to the first displayed line of text in the given element. This persists even if the text is reformatted. Applied to block-level elements only. Supported by IE5.5 and Opera 3.6.
P:first-line {color: red;}
<P>The first line of this paragraph is |
| first-letter | Applied to the first letter in the given element. Can be used to generate drop-cap effects, among others. Should be applied to block-level elements only. Supported by IE5.5+ and Opera 3.6.
P:first-letter {color: red;}
<P>The capital 'T' at the beginning of this paragraph is red.</P>
|
| Printing Properties | |
| page-break-after | Printing properties currently work partially with IE4 and more
fully with IE5+ and Opera 3.5. CSS2 will greatly augment
single-source strategies for documenters. Example: |
| page-break-before |
Values: same as above. Note that neither of these properties
work within tables. Also buggy used with <br> tag. Better
luck using page breaks in structural tags (H1, P, etc.). |
| Miscellaneous | |
| cursor |
Specifies the appearance of the cursor when placed within an element. Values: auto (browser determines based on context); crosshair; default (usually an arrow - determined by operating system); help; move; pointer; text; wait; e-resize; ne-resize; nw-resize; n-resize; se-resize; sw-resize; s-resize; w-resize. Use 'hand' to force the hand cursor, which works for IE4+ and Opera 3.5 although not part of the W3C specs. |
Author: bmerkey@tampabay.rr.com
Last Updated25/02/2009 - CSS - Reference I - Web Development - Neils Resource Web